Quickstart
First install qlasskit using pip.
pip install qlasskit
We now define a qlassf function that sums two numbers:
from qlasskit import qlassf, Qint, Qint2
@qlassf
def sum_two_numbers(a: Qint[2], b: Qint[2]) -> Qint[2]:
return a + b
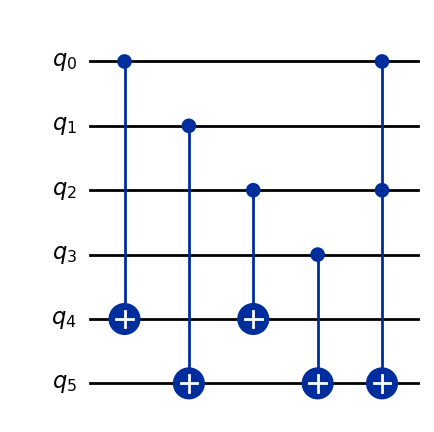
We can now export the resulting quantum circuit to any supported framework:
circuit = sum_two_numbers.export("qiskit")
circuit.draw("mpl")
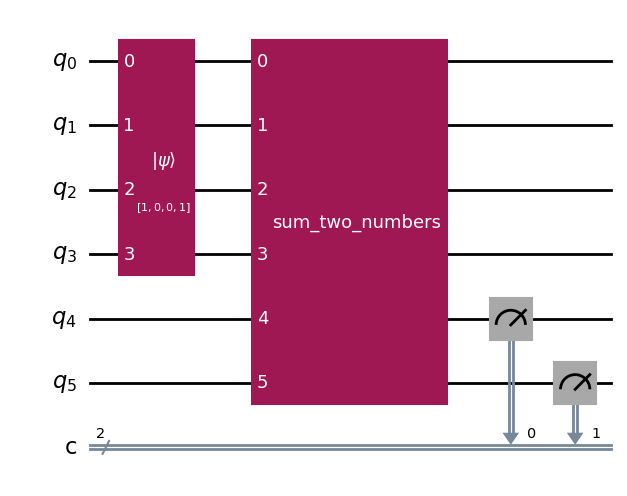
The qlassf function can be also exported as a gate, if the destination framework supports it. We can use encode_input and decode_output in order to convert from/to high level types of qlasskit without worrying about the binary representation.
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit
qc = QuantumCircuit(sum_two_numbers.num_qubits, len(sum_two_numbers.output_qubits))
qc.initialize(
sum_two_numbers.encode_input(Qint2(1), Qint2(2)), sum_two_numbers.input_qubits
)
qc.append(sum_two_numbers.gate("qiskit"), sum_two_numbers.qubits)
qc.measure(sum_two_numbers.output_qubits, range(len(sum_two_numbers.output_qubits)))
qc.draw("mpl")
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit, transpile
from qiskit.visualization import plot_histogram
from qiskit_aer import AerSimulator
simulator = AerSimulator()
circ = transpile(qc, simulator)
result = simulator.run(circ).result()
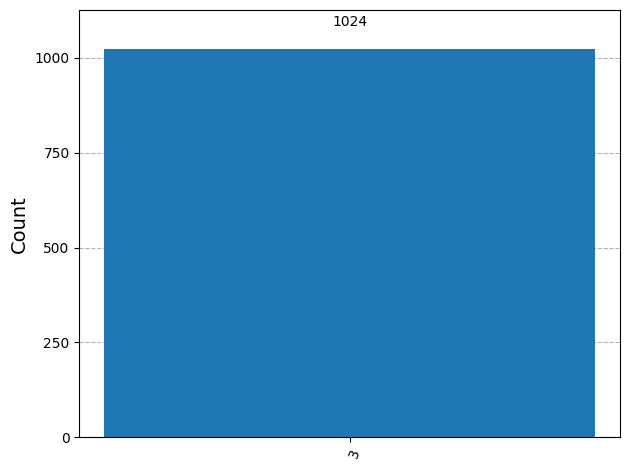
counts = result.get_counts(circ)
counts_readable = sum_two_numbers.decode_counts(counts)
plot_histogram(counts_readable)